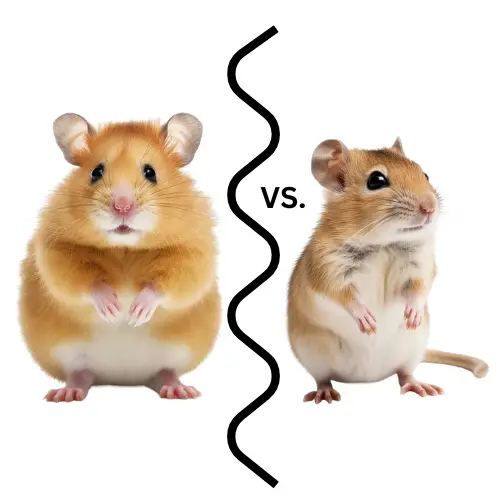
Small rodents have long captured the hearts of pet enthusiasts around the world. These pint-sized creatures, with their adorable looks and charming personalities, make fantastic companions for many people. Among the most popular choices for small rodent pets are hamsters and gerbils. These tiny critters bring joy and entertainment to countless households. But have you ever wondered what sets a hamster apart from a gerbil?

Table of Contents
Hamsters and Gerbils
Let’s begin by getting to know our two main characters: hamsters and gerbils. Hamsters belong to the rodent family Cricetidae and are known for their small, stout bodies and short tails. They come in various breeds, including Syrian hamsters, Roborovski hamsters, and Dwarf hamsters, each with its own unique characteristics. Gerbils, on the other hand, are small desert rodents belonging to the subfamily Gerbillinae. They have a more slender body structure and longer tails compared to hamsters. Popular gerbil breeds include Mongolian gerbils and Fat-tailed gerbils.
What is the Difference Between Hamsters and Gerbils?
Now that we’ve acquainted ourselves with hamsters and gerbils, let’s delve into the intriguing question of how they differ from each other. While they may share some similarities due to their rodent heritage, there are distinct characteristics that set them apart. From their physical attributes to their natural habitats, behaviors, and care requirements, exploring the disparities between these small creatures will help you make an informed decision about which one might be the perfect pet for you.
In the upcoming sections, we will embark on an exploration of the differences between hamsters and gerbils. We will examine their physical characteristics, including size, body structure, and fur types. We will also delve into their natural habitats and behaviors, shedding light on their preferences for burrowing or sandy environments, activity patterns, and social behaviors. Furthermore, we will discuss their average lifespans and specific care requirements, covering aspects such as housing, diet, and exercise needs.
By the end of this exploration, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what distinguishes a hamster from a gerbil. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to decide which small rodent pet aligns with your preferences, lifestyle, and ability to provide the necessary care.
So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and uncover the fascinating differences between hamsters and gerbils. Whether you find yourself captivated by the charm of hamsters or the allure of gerbils, there’s no doubt that either of these small companions will bring joy and companionship into your life.
Physical Characteristics
The typical size and body structure of hamsters
Hamsters are small rodents with a distinct body structure. The size of hamsters can vary depending on the breed. Syrian hamsters, also known as golden hamsters, are the largest of the common hamster breeds, measuring around 5 to 7 inches (13 to 18 cm) in length. Dwarf hamsters, such as Roborovski, Campbell’s, and Winter White hamsters, are smaller, ranging from 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm) in length.
The Different Types of Hamsters
In terms of body structure, hamsters have a compact and stout build. They have a round body shape with a pronounced abdomen. Their limbs are short, and their paws are equipped with sharp claws, which aid them in digging and climbing. One distinguishing feature of hamsters is their short tail, which is typically only a few centimeters long or even absent in some breeds.
When it comes to fur, hamsters exhibit various colors and textures depending on the breed. Syrian hamsters can be found in a wide range of colors, including golden, cream, cinnamon, black, and even white. Their fur is generally dense and plush. Dwarf hamsters, on the other hand, display different fur types. Roborovski hamsters have short, dense fur, while Campbell’s and Winter White hamsters have a thicker, more velvety coat.
The typical size and body structure of gerbils
Gerbils, unlike hamsters, possess a more elongated and slender body structure. They are generally larger than hamsters, but their size can also vary depending on the breed. Mongolian gerbils, the most common breed kept as pets, usually measure around 4 inches (10 cm) in length, excluding their tails. Fat-tailed gerbils, as their name suggests, have a plumper body structure and can grow up to 6 inches (15 cm) in length.
Gerbils have a sleek and agile build. Their bodies are elongated with a slender abdomen. They have longer limbs and paws, which are adapted for digging and running. One notable physical feature of gerbils is their long, tufted tail. The tail of a gerbil can measure around 4 to 5 inches (10 to 13 cm) in length and is covered in fur, unlike the short tail of hamsters.
Similar to hamsters, gerbils exhibit a variety of fur colors and textures. Mongolian gerbils are commonly found in shades of agouti, which is a mix of brown, gray, and white. They may also have solid colors like black or white. Fat-tailed gerbils, on the other hand, have a thicker and woollier coat, which provides them insulation in their natural desert habitat.
The key physical differences between hamsters and gerbils
Hamsters and gerbils have distinct physical differences that set them apart. Firstly, their body shapes differ significantly. Hamsters have a rounder and more compact body shape, while gerbils have a slender and elongated body structure.
Secondly, their tails exhibit a notable contrast. Hamsters have short tails that are either a few centimeters long or absent altogether, whereas gerbils have long, tufted tails measuring several inches in length.
Lastly, their facial features also display dissimilarities. Hamsters have rounder faces with prominent cheeks, while gerbils have more elongated and slender faces.
These key physical differences make it relatively easy to distinguish between hamsters and gerbils, even at a glance. Understanding these distinctions is essential when choosing a pet, as their physical characteristics can impact their behavior, care requirements, and overall compatibility with your lifestyle and preferences.
Considering the contrasting body shapes, tail lengths, and facial features of hamsters and gerbils, it becomes evident that these two small rodents have evolved distinct physical adaptations to suit their respective natural habitats and lifestyles. Hamsters’ compact bodies and short tails make them well-suited for burrowing and navigating through tight spaces in underground burrows. On the other hand, gerbils’ slender bodies and longer tails assist them in agility and balance, particularly in their desert habitat where they need to move swiftly and efficiently.
When deciding between a hamster and a gerbil as a pet, it is crucial to consider these physical disparities. For individuals seeking a small rodent with a rounder, cuddly appearance and a less active lifestyle, hamsters might be the ideal choice. Their shorter tails and round faces give them an endearing and huggable appeal. Hamsters also come in various sizes and colors, providing a wide range of options to suit personal preferences.
On the contrary, those looking for a more active and agile pet may be drawn to gerbils. Their longer bodies, tails, and more slender faces give them a sleek and athletic appearance. Gerbils are known for their remarkable jumping ability and agility, making them entertaining to watch as they explore and play in their enclosures.
Natural Habitat and Behavior
The natural habitat of hamsters
Hamsters are native to various regions, including parts of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. They have adapted to different environments, from grasslands to semi-deserts.
Hamsters are renowned for their burrowing instincts. In their natural habitat, they create intricate tunnel systems underground, which serve as their homes and provide protection from predators. These burrows often consist of multiple chambers for nesting, food storage, and waste disposal.
The natural habitat of gerbils
Gerbils originate from arid regions, such as the deserts and steppes of Asia and Africa. They are well-adapted to dry and sandy environments, including the Mongolian desert and the Sahara.
Gerbils have a preference for habitats with loose, sandy soil. They are excellent diggers, using their sharp claws and strong hind legs to create burrows in the sand. These burrows serve as shelter from extreme temperatures and predators, while also allowing gerbils to find food and store it for later consumption.

The behavioral traits of hamsters and gerbils
Activity patterns: Both hamsters and gerbils are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are more active during the night. This behavior is believed to have evolved as a survival strategy, enabling them to avoid daytime predators. During the day, they tend to sleep in their burrows.
Social behavior and hierarchy: Hamsters are generally solitary animals and prefer to live alone. They can become territorial and may exhibit aggressive behavior when sharing a space with other hamsters. On the other hand, gerbils are social creatures that live in groups called colonies. They exhibit complex social structures and engage in activities like grooming, playing, and huddling together for warmth. Gerbils establish a social hierarchy within their colonies, with dominant and subordinate individuals.
While hamsters and gerbils share similar activity patterns, their social behaviors greatly differ. Hamsters are solitary and prefer a solitary lifestyle, while gerbils thrive in social groups. It is important to consider these behavioral traits when choosing between a hamster and a gerbil as a pet, as it impacts their well-being and their ability to thrive in different living conditions.
Lifespan and Care Requirements
The average lifespan of hamsters
The average lifespan of hamsters varies depending on the breed. Syrian hamsters typically live for about 2 to 3 years, while Dwarf hamsters have a slightly shorter lifespan of around 1.5 to 2 years. However, with proper care and a healthy environment, some hamsters can live up to 4 years or even longer.
Factors that can influence a hamster’s lifespan include genetics, diet, exercise, living conditions, and overall health. Providing a balanced diet, a clean and spacious habitat, regular veterinary check-ups, and mental stimulation can help ensure a hamster’s well-being and potentially extend its lifespan.
The average lifespan of gerbils
Gerbils generally have a longer lifespan compared to hamsters. On average, gerbils live for about 2.5 to 4 years. Some gerbils have been known to reach 5 years or more with proper care and a healthy lifestyle.
Similar to hamsters, factors such as genetics, diet, exercise, living conditions, and healthcare can influence a gerbil’s lifespan. Providing a suitable habitat, a nutritious diet, opportunities for exercise and mental stimulation, as well as regular veterinary care, are crucial for ensuring the well-being and longevity of gerbils.
The care requirements for hamsters and gerbils
Both hamsters and gerbils have some similar care requirements. They both require appropriate housing with ample space to move and explore, as well as bedding materials for burrowing. A balanced diet consisting of commercial rodent pellets, fresh vegetables, fruits, and occasional treats is essential for both species. Providing opportunities for exercise, such as exercise wheels and tunnels, is beneficial for their physical and mental well-being.
However, there are also some specific differences to consider. Hamsters are more solitary and generally prefer to live alone, whereas gerbils are social animals and thrive in pairs or small groups. This means that if you choose to keep gerbils, you’ll need to provide companionship by housing them together. Additionally, gerbils have a higher need for sand baths due to their natural habitat in sandy environments.
Popularity as Pets
The popularity of hamsters as pets
Hamsters have a long history of being kept as pets, dating back to the 1930s. They gained popularity due to their small size, low maintenance requirements, and adorable appearance. Throughout the years, they have become one of the most commonly owned small rodents.
Hamsters are readily available in pet stores, making them easily accessible to prospective owners. They come in a variety of breeds, colors, and coat types, offering a wide range of options for those seeking a hamster as a pet. Their popularity is also due to their suitability for individuals or families looking for a low-commitment pet that requires less space and attention compared to larger animals.
The popularity of gerbils as pets
Gerbils have been gaining popularity as pets in recent years. While they have been kept as pets for a long time, their charming characteristics and unique behavior have attracted more attention from pet owners seeking an alternative to hamsters or other small pets.
Gerbils have specific traits that make them appealing to pet owners. They are known for their active nature, agility, and curiosity. Their social behavior and the ability to keep them in pairs or small groups have also contributed to their rising popularity. Additionally, their longer lifespan compared to hamsters is appealing to those seeking a longer-term commitment.
The overall popularity of hamsters and gerbils as pets
Hamsters have a longstanding popularity as pets, thanks to their long history as companion animals, wide availability, and diverse breeds. They have established themselves as one of the most popular small rodents kept as pets, offering an array of options to potential owners.
Gerbils, while not as historically prevalent as hamsters, have been growing in popularity due to their unique traits and appealing characteristics. Their active nature, social behavior, and longer lifespan have captured the interest of pet owners seeking a more interactive and long-term companion.
In terms of overall popularity, hamsters maintain a strong presence as a classic and widely recognized pet choice. However, gerbils have been steadily increasing in popularity, attracting a growing number of enthusiasts who appreciate their distinctive qualities.
Ultimately, the choice between hamsters and gerbils as pets depends on individual preferences, lifestyle, and the specific traits that resonate with each owner. Both small rodents offer companionship, entertainment, and joy, making them delightful additions to many households.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of hamsters and gerbils, we have uncovered several key differences between these small rodent species. In terms of physical characteristics, hamsters typically have compact bodies, shorter tails, and round faces, while gerbils have slender bodies, longer tails, and more elongated faces. They also differ in their natural habitats, with hamsters being burrowers adapted to various environments and gerbils thriving in dry, sandy habitats. Additionally, their behaviors vary, with hamsters being more solitary and nocturnal, while gerbils are social animals that live in colonies. Care requirements also differ slightly, with gerbils needing companionship and sand baths, while both species require appropriate housing, a balanced diet, exercise, and veterinary care.
Both hamsters and gerbils have earned their places as beloved and popular small pets. Hamsters have a long history as companion animals, offering a range of breeds and colors, and are widely available in pet stores. Gerbils, although gaining popularity in recent years, have captivated pet owners with their active nature, social behavior, and longer lifespan. Both species bring joy, entertainment, and companionship to countless households around the world.
When deciding between a hamster and a gerbil as a pet, it is important to take into account your own preferences, lifestyle, and the specific traits that align with your expectations. Consider factors such as physical appearance, social behavior, activity levels, and the level of commitment you are willing to provide. Reflect on the care requirements and the time and effort you can dedicate to their well-being. By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that ensures a harmonious and fulfilling relationship between you and your chosen small rodent companion.
Whether you choose a hamster or a gerbil, both species have their unique charm and can bring joy and companionship to your life. Embrace the opportunity to welcome a new member into your family and create memorable experiences with your small, furry friend.